- High design complexity of design-build millwork projects demands a collaborative approach between designers, engineers, and builders for accurate estimation.
- Utilizing digital tools, and cost estimation software enhances accuracy and efficiency.
- Regular training to estimators for handling the complexities of modern millwork projects deliver successful project outcomes and client satisfaction.
Design-build millwork projects involve heavy and complex design customization, fluctuating material costs, and varying labor requirements. The integration of design and construction phases requires close coordination, which can be difficult to quantify, and frequent design changes complicate initial millwork estimating. Additionally, design-build millwork projects must often be coordinated with other trades, and compliance with local building codes adds another layer of complexity.
Table of Contents
- Significance of Design-Build Project Estimation
- Challenges in Millwork Estimation
- Key Components of Millwork Project Estimation
- Steps in Millwork Estimating for Design-Build Projects
- How to Calculate Material Quantities in Design-Build Millwork Projects
- Tools and Software for Millwork Estimating
- Best Practices for Accurate Millwork Estimation for Design-Build Projects
- Conclusion
Detailed planning, use of historical data and close collaboration between design and construction teams ensure accurate millwork estimation and quantity takeoff. Regular reviews and updates of the estimate, along with contingency planning for potential changes and risks, help improve the accuracy and reliability of estimates.
Significance of Design-Build Project Estimation
A precise estimate provides a solid foundation for allocating resources effectively, ensuring that the project stays within budget while meeting client expectations. It impacts overall project costs by identifying potential expenses early on, allowing for better financial management and minimizing the risk of cost overruns.
Additionally, accurate estimation influences project timelines by enabling realistic scheduling and resource allocation, which helps prevent delays. Ultimately, a well-crafted estimate fosters better decision-making, enhances efficiency, and contributes to the successful completion of design-build millwork projects.
Challenges in Millwork Estimation
- Variability in Material Costs: Market fluctuations can cause significant changes in material prices, affecting overall project costs.
- Labor Availability and Costs: Skilled labor shortages can lead to higher labor costs and project delays.
- Design Changes: Design modifications during the project can complicate the estimation process and lead to cost increases.
- Site Conditions: Unforeseen site challenges, such as difficult access or unexpected structural issues, can disrupt project plans.
Key Components of Millwork Project Estimation

Materials
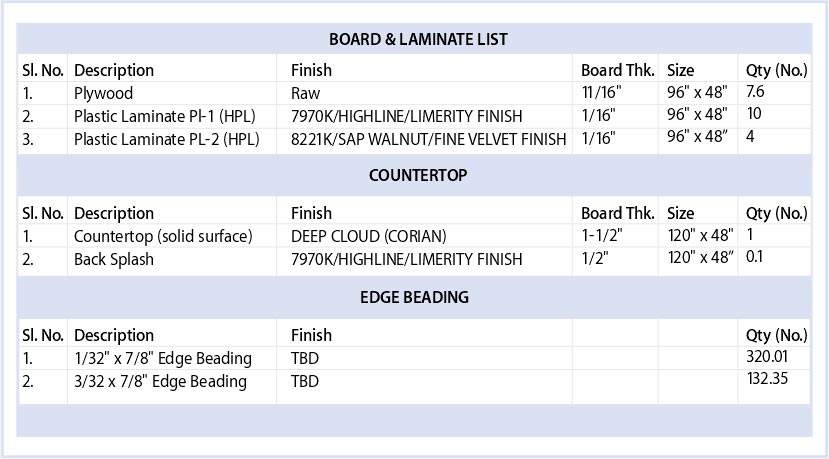
- Types of Materials: Commonly used materials include hardwood, plywood, MDF, veneers, and laminates.
- Costs and Sourcing: Consider material prices, availability, and reliable suppliers to ensure quality and budget adherence.
Labor
- Skilled Labor Requirements: Identify the need for carpenters, joiners, and craftsmen with specialized millwork skills.
- Cost Estimation: Calculate labor costs based on hourly rates, project complexity, and labor availability.
Time
- Project Timeline: Develop a detailed timeline that includes design, fabrication, and installation phases.
- Scheduling and Sequencing: Plan the sequence of millwork tasks to optimize efficiency and prevent delays.
Overhead and Profit
- Overhead Costs: Include expenses such as utilities, equipment maintenance, and administrative costs.
- Profit Margins: Determine profit margins based on project scope, competitive rates, and desired profitability.
Steps in Millwork Estimating for Design-Build Projects
Accurate millwork estimation is crucial for the successful execution of design-build projects. It involves a systematic approach to evaluating project requirements, quantifying materials and labor, and ensuring all potential costs are accounted for.
Following these detailed steps ensures precise budgeting, efficient resource allocation, and clear communication with stakeholders, ultimately leading to high-quality outcomes and client satisfaction. Here are the key steps involved in millwork estimating for design-build projects:
Step 1: Project Assessment
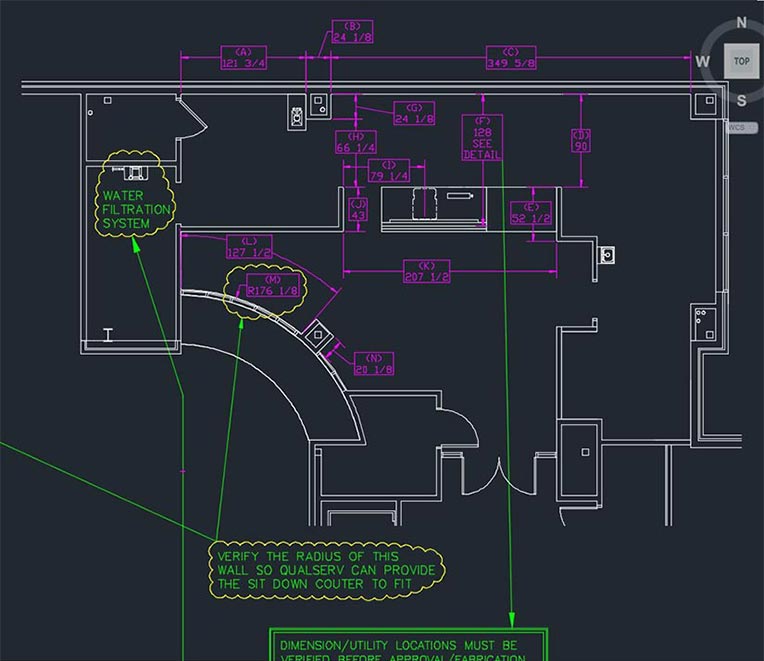
- Reviewing Project Plans and Specifications: Carefully examine architectural millwork shop drawings , blueprints, and detailed specifications to understand the scope and requirements of the millwork project. Identify any unique features or custom elements that need special attention.
- Site Visits and Measurements: Conduct thorough site visits to gather accurate measurements and assess site conditions. This helps to identify any potential challenges or constraints that may affect the project, such as access issues, existing structures, or environmental factors. (Red line drawings from Joinery PDF)

Step 2: Detailed Takeoff
- Breaking Down the Project into Components: Decompose the project into individual components and tasks, such as cabinetry, moldings, paneling, and custom fixtures. This detailed breakdown ensures that all elements are accounted for in the estimate. (Quantity take off from case study Quantity Takeoffs Solutions for Cabinet Manufacturer | HitechDigital)
- Quantifying Materials and Labor: Determine the quantities of materials needed for each component and estimate the labor required for fabrication and installation. Accurate quantification is essential for developing a reliable cost estimate.
Step 3: Cost Estimation
- Applying Unit Costs to the Takeoff Quantities: Assign unit costs to the quantified materials and labor based on current market rates and historical data. This step provides a baseline cost for each millwork material used in the project.
- Accounting for Waste and Contingencies: Include allowances for material waste, potential project changes, and unforeseen issues. Contingencies ensure that the estimate remains realistic and covers all possible scenarios.
No resource found with the provided tag.
Step 4: Proposal Preparation
- Compiling the Estimate into a Proposal Format: Organize the detailed cost estimate into a professional proposal format. The proposal should be clear, concise, and comprehensive, outlining all project components, costs, and deliverables.
- Including Terms and Conditions: Add terms and conditions to the proposal, covering payment schedules, timelines, warranties, and any other relevant contractual details. This helps set clear expectations and protects both parties.
Step 5: Review and Approval
- Internal Review Processes: Conduct internal reviews of the estimate and proposal to ensure accuracy and completeness. This step may involve multiple team members, including project managers, estimators, and financial officers, to validate the estimate. (Provide process charts for approval and review of estimates)
- Client Review and Approval: Present the proposal to the client for review. Be prepared to discuss and clarify any aspects of the estimate and make adjustments if necessary. Obtain formal approval to proceed with the project, ensuring all parties are aligned on the scope, costs, and timeline.

How to Calculate Material Quantities in Design-Build Millwork Projects
Calculating the quantity of materials needed for millwork design-build projects involves a detailed process to ensure accuracy and efficiency. Here’s a structured approach to help you with this task.
Assume you are calculating materials for a custom built-in bookshelf:
Specifications:
- Dimensions: 8 feet (height) x 4 feet (width) x 1.5 feet (depth)
- Material: 3/4 inch plywood
- Shelves: 5 adjustable shelves
Calculate Panels for the Sides:
- Height = 8 feet, Depth = 1.5 feet
- Area per side = 8 ft x 1.5 ft = 12 sq. ft.
- Total for two sides = 12 sq. ft. x 2 = 24 sq. ft.
Calculate Panels for the Top and Bottom:
- Width = 4 feet, Depth = 1.5 feet
- Area per panel = 4 ft x 1.5 ft = 6 sq. ft.
- Total for top and bottom = 6 sq. ft. x 2 = 12 sq. ft.
Calculate Panels for the Back:
- Height = 8 feet, Width = 4 feet
- Area = 8 ft x 4 ft = 32 sq. ft.
Calculate Panels for the Shelves:
- Width = 4 feet, Depth = 1.5 feet
- Area per shelf = 4 ft x 1.5 ft = 6 sq. ft.
- Total for 5 shelves = 6 sq. ft. x 5 = 30 sq. ft.
Sum Total Area:
- l area = 24 sq. ft. (sides) + 12 sq. ft. (top/bottom) + 32 sq. ft. (back) + 30 sq. ft. (shelves) = 98 sq. ft.
Add Waste Factor (10%):
- Waste = 98 sq. ft. x 0.10 = 9.8 sq. ft.
- Total material required = 98 sq. ft. + 9.8 sq. ft. = 107.8 sq. ft. (round to 108 sq. ft.)
Tools and Software for Millwork Estimating
| Method | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Manual Estimation Techniques |
Pros
|
Cons
|
| Digital Tools |
Pros
|
Cons
|
Millwork contractors and estimators rely on a range of specialized software to achieve accurate millwork estimates. Many of the tools have estimating capabilities along with design features to integrate digital takeoff, detailed estimating, and project management, making them indispensable for millwork projects. These tools collectively empower professionals to deliver exceptional results, optimizing both design and production processes in the millwork industry.
- Microvellum: A comprehensive software that combines design, engineering, and production automation specifically for the woodworking industry. It integrates with AutoCAD for detailed designs and generates accurate material estimates and production-ready data.
- Cabinet Vision: This software provides design, engineering, and production solutions for the wood manufacturing industry. It helps in creating detailed designs, optimizing material usage, and generating cost estimates.
- PlanSwift: A versatile takeoff and estimating software used in various construction trades, including millwork. It allows users to perform digital takeoffs and create detailed cost estimates.
- Swood: An add-on for SOLIDWORKS, Swood is designed for the woodworking and furniture industry. It provides tools for design, manufacturing, and estimating costs of custom wood products.
- 2020 Design: A software suite designed for kitchen and bathroom design but also widely used in custom millwork projects. It helps in creating detailed designs and generating material and cost estimates.
Best Practices for Accurate Millwork Estimation for Design-Build Projects
To achieve accuracy in millwork estimates, it is essential to follow best practices that enhance the precision and reliability of estimates. These practices majorly focus on fostering collaboration between various stakeholders and sharing updates/training to relevant people. By adhering to these, millwork contractors can deliver high-quality estimates that meet client expectations and stay within budget and timelines.
Early and Continuous Involvement
- Engaging Estimators Early in the Project: Involve estimators from the initial stages of the project to ensure accurate and realistic budgeting. Early involvement helps in identifying potential challenges and cost-saving opportunities.
- Continuous Updates and Revisions to Estimates: Regularly update and revise estimates as the project progresses and new information becomes available. Continuous monitoring ensures that the estimate remains accurate and reflective of any changes in scope or conditions.
Collaboration with Design and Construction Teams
- Importance of Communication and Teamwork: Foster open communication and strong teamwork between estimators, designers, and construction teams. Effective collaboration ensures that all parties are aligned and informed, leading to more accurate estimates.
- Sharing Information and Feedback Loops: Create a feedback loop where information is shared openly and feedback is encouraged. This helps in identifying potential issues early and making necessary adjustments to the estimate.
Detailed Documentation
- Maintaining Comprehensive Records: Keep thorough records of all estimates, including the assumptions and data used. Detailed documentation provides a clear trail for reviewing and refining estimates.
- Utilizing Checklists and Templates: Use standardized checklists and templates to ensure consistency and completeness in the estimation process. These tools help in covering all aspects of the project and reducing the risk of omissions.
Regular Training and Updates
- Keeping Up with Industry Trends and Standards: Stay informed about the latest industry trends, standards, and technological advancements. Regularly updating knowledge helps in making more informed and accurate estimates.
- Investing in Training for Estimators: Provide ongoing training and professional development opportunities for estimators. Investing in their skills and expertise ensures that they are equipped to handle the complexities of modern millwork projects.
Conclusion
Accurately estimating millwork for design-build projects is a complex yet essential task that requires a strategic approach. By following a structured process that includes thorough project assessment, detailed takeoff, precise cost estimation, comprehensive proposal preparation, and diligent review and approval, service providers can ensure successful project outcomes.
Leveraging modern estimation tools, integrating cost estimation software and CAD enhances estimation accuracy and efficiency. It allows you to not only mitigate risks and control costs but also stay on project delivery schedules.
Partner with us for cutting-edge estimation services
Let’s elevate your project accuracy and efficiency with zero room for errors.