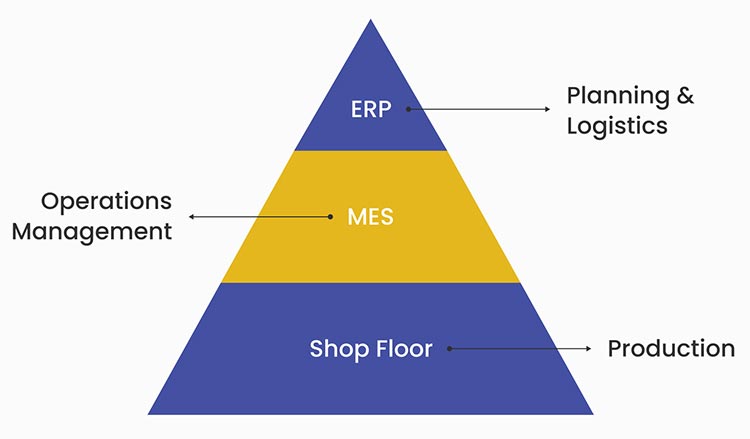
- MES and ERP – the two prominent data and operations management systems in the manufacturing industry are so interconnected that they often seem interchangeable.
- While ERP focuses on broader business functions that are beyond the shop floor, MES is centered on the execution and optimization of shop floor processes.
- The decision on whether to integrate ERP with MES for a more comprehensive solution or to select a standalone MES/ERP system should be based on your specific needs.
MES (Manufacturing Execution System) and ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) are two distinct but interconnected systems in the manufacturing industry. They are primarily known for the data integration and connectivity that improve productivity and collaboration. However, their functions and roles often overlap, making it difficult to choose one over the other for specific business needs.
Table of Contents
MES primarily focuses on the execution and optimization of shop processes, whereas ERP encompasses business functionalities beyond the shop floor. This difference in the core scope and functionalities of these systems is crucial to understand. If you are not clear about your goals, neither of these systems nor data integration can give positive business outcomes.
Let’s begin with the basics to understand what is ERP vs MES. We will then analyze how you can best utilize these systems for your specific business objectives.
About MES
What is MES?
MES, in its simplest form, is a software that empowers manufacturers with 360-degree visibility into the shop floor. It drives visibility into production processes and activities on the factory floor, ensuring that everything is running smoothly and efficiently.
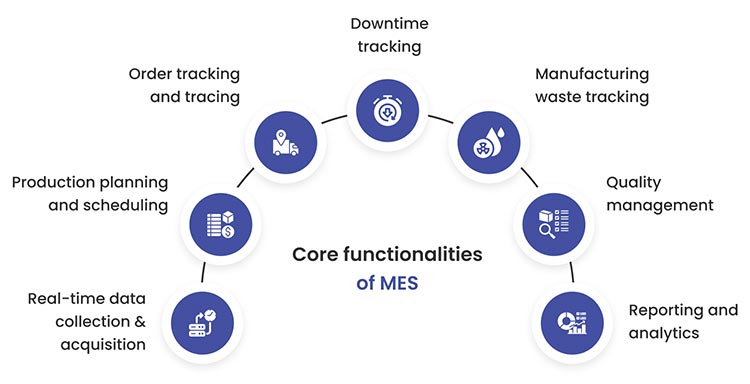
Manufacturing Execution System (MES) core functionalities
-
Real-time data collection for shop floor monitoring system: MES collects data from all the sources within the shop floor to give a clear picture of all activities. This may include resource availability, production orders, operator activities, and more. The data collected in MES, either manually or automatically, further supports detailed performance analysis for enabling improved and proactive production management.
-
Production Planning and Scheduling: We can divide this into three parts: labor or staff, machine, and inventory management.
- Inventory Management System: MES keeps track of inventory levels in real time, ensuring stocks neither run over or fall short.
- Labor Management System: MES manages the workforce by efficiently tracking their work hours, task assignment, training records, and more.
- Machine Management System: Ensures machines stay in good condition at all times by implementing real-time monitoring, maintenance scheduling, and alerts for issues, etc.
MES uses advanced machine learning algorithms and technologies like artificial intelligence to create optimized schedules. It also accounts for real-time constraints of labor, machine, and material for alleviating any hiccups. This ensures proactive capacity planning – minimizing idle time and time spent on changeovers, ultimately leading to improved and competitive delivery timelines.
-
Order Tracking and Tracing: Knowing the exact state of your order within production allows for better process management and enables informed decision making among stakeholders. Barcode and RFID technology integrates with MES to spare your machine operators from spending time on manual data entry and record tracing. Each item is assigned a unique identifier to monitor order progress, identify bottlenecks, and estimate delivery dates accurately.
-
Downtime Tracking: Machine downtimes are one of the main factors that contribute to delays in the order delivery process. With MES, you can prevent such delays and improve operational efficiency on the factory floor. MES integration with other systems empowers manufacturers with downtime tracking capabilities such as monitoring & tracking stoppages, recording stoppage duration, predicting equipment downtime, automating wrap-ups for downtime operations, etc. – all ensuring everything runs as expected and anomalies are detected beforehand.
-
Manufacturing Waste Tracking: This is another area where real-time monitoring and centralization of complete manufacturing data is important. Waste management is a critical process in the manufacturing industry. An inefficient process can negatively impact your organization’s bottom line. MES simplifies the waste management process within manufacturing companies by providing them with a clear visibility of waste, scrap, and spoilage across the stages a product goes through. Stakeholders can get alerts and notifications in real-time for any change in critical KPIs like OEE, FTTQ, and FPY giving them greater control over waste management.
-
Quality Management: MES ensures compliance with quality standards by enforcing control checkpoints and inspection criteria during critical production stages. With features like ‘advanced algorithms and conditional programming’ the system will automatically identify any anomaly in the process. It ensures that every product or order follows pre-defined steps in sequence and alerts the operator to any deviations. Some MES tools have a built-in collaboration functionality to raise and log issues for a job. This can be done within the system environment to get their supervisor’s attention without losing time.
- Overall Equipment Effectiveness: Another area where MES stands out in optimizing manufacturing processes is – OEE Management. While advanced algorithms enable manufacturers to create custom workflows for detecting potential anomalies in the production process, OEE management ensures that the quality of all equipment involved remains in good working order. MES generates OEE scores for all the manufacturing equipment involved in a particular manufacturing operation. The score helps manufacturers measure the effectiveness of associated plants, optimize team performance, enhance production capacity, ultimately reducing downtime and operational costs.
-
Reporting and Analytics: Effective production management cannot rely on relevant data alone. Stakeholders need analytical insights for reports to make decisions on enhancing overall efficiencies. MES uses consolidated data from various sources to generate real-time insights on key performance metrics like OEE, yield, and cycle time. Easy and collaborative access ensures that all decisions are data-driven.
MES benefits for manufacturing
- Improved efficiency: MES streamlines production operations, reduces downtime, minimizes production bottlenecks, and automates rule-based tasks, leading to increased productivity.
- Enhanced quality: An IIoT-enabled MES ensures better control and monitoring which results in enhanced process quality and fewer defects.
- Reduced operational costs: The ability to trace and track orders, materials, and labor leads to reduced waste and operational costs.
- Compliance: MES ensures adherence to industry regulations and quality standards, reducing the risk of noncompliance issues.
- Data-driven decision making: MES provides data-driven insights, enabling better decision making and continuous process improvement.

Implementing an MES for job shop owners
- Do you still manually plan production?
- Can you track and trace all manufacturing orders?
- How updated are your reports on machine availability?
- Ask many more questions like this to assess your job shop’s maturity.
About ERP
What is ERP?
ERP is another business processing software that automates and simplifies back-end processes for departments such as accounting, HR, procurement, and supply chain. ERP systems readily integrate with other enterprise software solutions, such as CRM, to collect and merge data for a comprehensive business view. Furthermore, its robust reporting capabilities lets you delve deeper into key performance insights and identify potential bottlenecks or areas of improvement.
Enterprise Resources Planning (ERP) core functionalities
![Enterprise Resources Planning [ERP] functionalities](https://www.hitechdigital.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/11/enterprise-resources-planning-erp-functionalities.jpg)
- Centralizes enterprise-wide data: ERP integrates core business applications and centralizes complete data for seamless information flow and collaboration. With an ERP, manufacturers can seamlessly access all operational data, such as financial transactions, inventory levels, procurement processes, and customer orders, all from the same system.
- Automates routine back-office tasks: By maintaining a central repository of data for accounting, finance, and HR, ERP empowers businesses to automate repetitive tasks. This may include anything from payroll, generating invoices, processing orders, and others, for improved productivity and reduced errors.
- Comprehensive aggregate-level reporting: ERP offers strategic insights into business performance, with an emphasis on financial planning, which empowers stakeholders to make better informed decisions based on historical trend analysis.
ERP benefits for manufacturing
- Streamline inventory management: Helps get the most out of the inventory by closely analyzing order demands and fluctuations, if any.
- Precise business planning: With improved supply chain coordination and proactive supplier relationship management, business processes are streamlined, which further ensures just-in-time order delivery.
- Boosts operational efficiency: Improves the overall operational efficiency by automating regular tasks and workflows at the enterprise level.
MES VS ERP: Highlighting the key differences
Both ERP and MES help businesses with data integration and a unified view of information for efficiently managing business operations. However, there are some key differences that set them apart. Such as:
| Key differentiators | ERP | MES |
|---|---|---|
| Focus and scope | ERP Integrates enterprise-wide data, including finance, sales, inventory management, supply chain management, and more. (Focus on financial planning) | MES Provides a means to monitor and control the entire production process (focus on production visibility / improvement) |
| Tech connectivity | ERP Built to combine with other systems, such as CRM, accounting, supply chain management, etc. | MES Integrates directly with shop floor machines, although flexible to integrate with other systems/applications, SCADA, PLCs, etc. |
| The way they feed on data | ERP Uses historical data for long-term planning and decision making | MES Uses real-time as well as historic data for tracking short-term trends |
| Reporting & analytics | ERP Provides aggregated information on a monthly/quarterly basis, focusing on longer-term planning, trend analysis, and forecasting. | MES Provides granular production-level insights on an hourly or even minute basis, with a focus on real-time information. |
| Cost-effectiveness | ERP More expensive because of the complex integration needs catering to a broader business segment. | MES Less expensive as designed to take care of specific segments of the manufacturing process |
| User base | ERP Facilitates efficient resource planning at the enterprise level. Usually used by management and C-Suite. | MES Dedicated to optimizing manufacturing operations. Used by operators, supervisors, project managers, schedulers, and management |
| Customization / Scalability | ERP More standardized for non-core processes and is not always industry specific. | MES Customizable and configurable to align with different manufacturing processes in various industries. It is important to choose MES that aligns with your specific industry. |
Get answers to all your MES questions at one place.
Read about the comprehensive role of MES software – a game-changing solution for metal fabrication and woodworking industries.
Two ways to choose the right system – MES and/or ERP
Option 1: Using ERP with MES
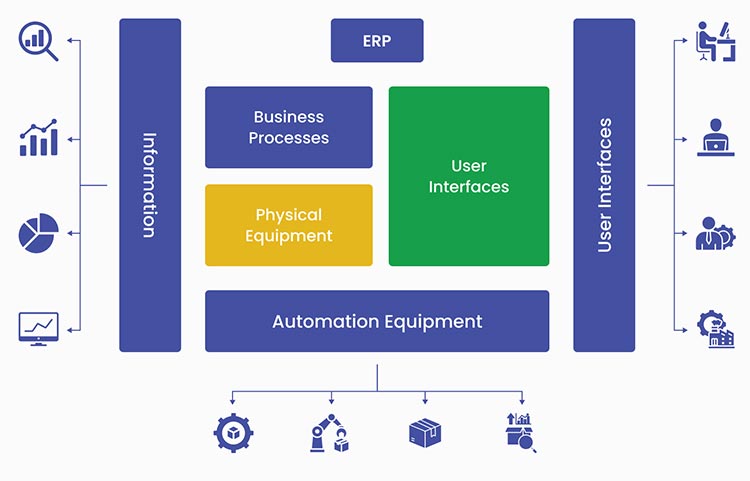
If we have to pick a single standalone system – An ERP is the clear winner. This is because it offers integration with a broader set of systems and business processes than MES.
The only area where an ERP falls short is on the factory floor. It cannot effectively guide operators, identify bottlenecks, do quality checks or last-minute product adjustments. ERP does not perform when it comes to monitoring shop floor activities.
This is the reason certain manufacturing businesses prefer to integrate ERP with MES to get the best of both worlds. So, let’s understand the benefits of integrating ERP with MES:
-
Integrated business processes – from back office to shop floor
MES and ERP integration allows data to seamlessly flow across systems, departments, and stakeholders. Their integration eliminates the need to manually collect or enter data if the two systems are able to talk to each other. For example, when a customer places an order, the details are saved in the ERP system. Based on this, the ERP system generates a production schedule for the order, which is automatically received by the integrated MES. From here onwards, everyone on the shop floor stays informed about the order progress through real-time data shared by the MES system.
-
Enhanced shop floor visibility
While ERP excels at managing inventory and sales orders, MES can simplify production planning and schedules. Integrating both systems means filling up the gaps each system possesses when used alone – ultimately improving the visibility of shop floor operations. For example, any specific instructions or job details for a customer in ERP can be easily integrated with MES. This will enable the operators to understand the nuances that they need to have visibility into.
-
Precise inventory management
Inventory management means ensuring that your stocks are neither in excess nor too low. By combining the MES and ERP systems, you can enable accurate tracking of inventory levels throughout the production process – ultimately reducing the risk of stock-outs/ excess inventory. With the changes in the job status from production planning to dispatch, keep all inventory status up to date. This will avoid large, unused inventory on the shop floor.
-
More informed decision-making in manufacturing
Both MES and ERP systems have comprehensive reporting and analytics capabilities. While ERP provides historical reports on the processes beyond the shop floor, MES’ intuitive reporting dashboard provides real-time insights into shop floor activities. Combining both ERP and MES empowers manufacturing stakeholders with more visibility and control over manufacturing and business processes.
-
Efficient order journey management
An order created in the ERP system can be seamlessly transferred to the MES for further execution on the factory floor. So, the details like product specifications, quantities, and delivery deadlines, are accurately passed to the manufacturing team to reduce lead times.
Integrate MES with your existing ERP system.
Leverage your ERP data to unlock powerful insights for informed decision-making and to avoid production hiccups.
Option 2: Using a standalone MES or ERP
Every business has unique organizational needs, and data handling requirements, sometimes rendering an integrated MES-ERP system unnecessary. Hence, it is imperative to rigorously evaluate your specific business needs before implementing one or both.
Standalone MES and ERP systems can work well, provided your business objectives align with their respective core functionalities.
Choose a standalone MES if:
- Shop floor optimization is a priority for you.
- You need immediate, near-real-time visibility in all shop floor operations, including machine performance, material availability, etc.
- Enforcing quality checkpoints and compliance are a necessity for you.
- Accurately predicting and managing production schedules is exceptionally important for you.
- You have specific shop floor challenges or gaps in your manufacturing processes that only a customized MES solution can address.
Advantages of choosing this route
- Minimal hassles (time & effort) of integration
- Easy and quick to implement for standard problem areas. However, the implementation can take a significant amount of time in the case of an end-to-end transformation. (We can link an article here that says it can take 3-5 years to successfully implement an ERP). For example, if you’re happy with your processes but would like to have improved scheduling tools, you can use just the scheduling software from the MES package.
- Supports industry-specific optimization; comparatively easier to implement and adopt to give you an experience of just another extension of your own processes
Are you looking to implement MES for your job shop?
Struggles of implementing MES can go in circles with no end in sight. Know the common pitfalls in MES implementation and avoid them for a successful deployment.
FAQs on MES & ERP
Do you need MES when already using an ERP system?
No, not necessarily. It depends on your current business requirements. However, if you want to have a clear visibility on shop floor operations – consider integrating your existing ERP with MES for better operational visibility.
What is the purpose of MES?
To control, refine, and optimize production and shop floor processes for better order and job management. It provides stakeholders with a comprehensive platform to collaborate with and access real-time information on shop floor activities.
How do MES and ERP work together?
Both the MES and ERP systems complement each other. Integrating both systems actually helps to fill the gaps they have when working individually. MES provides real-time shop floor data to ERP, which can further be shared across the systems integrated with ERP. This data exchange leads to proactive production planning, inventory management, and machine maintenance.
However, if you do not have a need for two extensive systems, you can also choose to go with the standalone option of either MES or an ERP.
What is the difference between MES and an ERP?
The core difference between MES and an ERP system lies in the way they integrate with applications. An ERP system integrates with almost every business application, while MES integrates directly with manufacturing machines with a focus on optimizing and real-time monitoring of manufacturing processes.
Which ERPs can I integrate with MES?
All widely used ERP systems, such as SAP, Oracle NetSuite, Microsoft Dynamics / Business Central 365 can be integrated with MES to enable effective production management. However, to ensure a frictionless integration process, analyze the versions and configuration of these software packages. Consult with your vendor about the precise compatibility information in advance.
How can I easily migrate data from ERP to MES?
Start by creating a detailed data mapping plan so you know exactly what data needs to be migrated. Use suitable tools to extract the identified data from the ERP, covert it into a suitable format – something that’s compatible with the end MES software. Once done, import the data, validate its accuracy, and keep monitoring it to ensure consistency. These steps may vary depending upon your unique business needs and the type of software packages involved. Discuss this migration process with your vendor to avoid last-minute hiccups.
How easily can I import all of my data into MES?
Modern MES software comes with smart features that make importing data a breeze for businesses – especially if the imported data is simple data. However, the ease of import may vary when dealing with complex sets of data. It also depends on the capabilities of the specific MES software to which your machines are about to connect. Hence, closely analyze the prerequisites, database compatibility, and other integration parameters while choosing MES vendor.
Why can’t I just create order schedules from an ERP?
This is because the process of building order schedules using an ERP system is quite complex, especially if you want to run complex schedules with advanced algorithms and parameters like demand fluctuations, lead times, etc. This level of customization and flexibility is generally available in MES, which simplifies the order scheduling and, hence is often recommended over ERPs.
Conclusion
Within the manufacturing landscape, both MES and ERP systems play distinct yet critical roles in enhancing the overall efficiency of business operations. While manufacturing ERPs take care of order and inventory management at the top level, MES helps refine real-time shop floor operations. However, there are specific areas where MES and ERP systems often collaborate to provide more valuable insights into manufacturing operations compared to their individual contributions.
Choosing one integrated approach over another depends on your specific business demands and strategy. Closely analyze your business requirements, along with the core focus and scope of each system before implementing a system. Remember, implementing a new MES or ERP solution can be challenging. Therefore, evaluate your integration and specific business needs carefully to decide which system best for your manufacturing business.





