- Manual data collection is best for small-scale projects that prioritize accuracy and nuance.
- Web scraping is ideal for large-scale data collection but requires maintenance and raises ethical concerns.
- AI-powered data collection is adaptable and efficient but requires higher upfront investment.
High-quality and readily available information is crucial for making informed decisions for business, researchers and others. How you collect your data determines the reliability of your information, and the depth and accuracy of your insights into market trends, customer behavior, and internal processes.
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Different Data Collection Technologies and Methods
- AI vs Web Scraper vs Manual Data Collection – A General Comparison
- A Comparative Analysis of AI vs Web Scrapers vs Manual Data Collection
- Use Cases and Applications – Manual Data Collection vs AI vs Web Scrapers
- How to Choose the Right Data Collection Method for Your Needs
- Wrapping Up
Traditional data collection methods like surveys, interviews, and observations are often time intensive and susceptible to human error. Modern techniques like web scraping automatically extract data from websites, rapidly providing large volumes of information.
AI data collection utilizes machine learning algorithms to gather and analyze data from diverse sources, including images, videos and text. This reveals complex patterns and trends that might otherwise go unnoticed.
When choosing the best way to collect data, it’s thus important to thoroughly understand the nuances of manual data collection vs. AI, web scrapers vs. manual data collection, and AI vs. web scrapers against factors like efficiency, speed, data quality, scalability and budget constraints.
This allows you to select the most efficient and cost-effective method for your project.
Understanding the Different Data Collection Technologies and Methods
Understanding different data collection methods is crucial because it allows you to choose the most appropriate technique for your specific project or research.
1. Manual Data Collection
Manual data collection is a hands-on approach that involves researchers directly gathering data, often in natural environments.
Techniques include observation and interviews, which can be structured, semi-structured, or in-depth, each designed to capture specific types of information.
Focus group discussions for understanding shared perspectives and group experiences represent another manual method. The choice of method depends on the research question, the study population and available resources.
2. Web Scraping
Web scraping involves programmatically extracting data from websites. One of the fundamental web scraping techniques is parsing HTML, where you utilize libraries like BeautifulSoup to pinpoint and extract specific data from a webpage’s HTML structure.
Web scraping tools necessitate navigating intricate website structures, achieved by following hyperlinks and interacting with a website’s DOM elements.
Modern websites employ JavaScript to load content dynamically. To scrape these sites, tools like Selenium render the JavaScript and capture the fully loaded HTML, enabling data extraction.
Ethical considerations and legal implications, such as website terms of service and data privacy regulations, guide responsible web scraping practices.
3. AI-Driven Data Collection
AI-driven real estate data collection utilizes machine learning algorithms to automate and enhance the process of collecting data from various sources. Pattern recognition helps identify recurring trends or structures within datasets. This targeted approach helps filter out unnecessary noise.
Data classification categorizes data points into predefined classes based on learned features. This facilitates organized and efficient data storage and retrieval, making data management more streamlined.
Anomaly detection focuses on identifying outliers or deviations from established patterns within datasets. This capability helps uncover fresh insights and detect errors that might otherwise go unnoticed.

How to Leverage online Clustering algorithms and APIs to tackle fluctuating volumes in real estate data aggregation
- MLS APIs and web scraping together enhance the accuracy of real estate listings.
- Clustering APIs provide direct access to MLS data, web scraping captures additional information.
- The combination ensures comprehensive, current property details, improving data quality.
AI vs Web Scraper vs Manual Data Collection – A General Comparison
The following table lists the common differences between manual data collection, web scraping and AI-driven data collection methods:
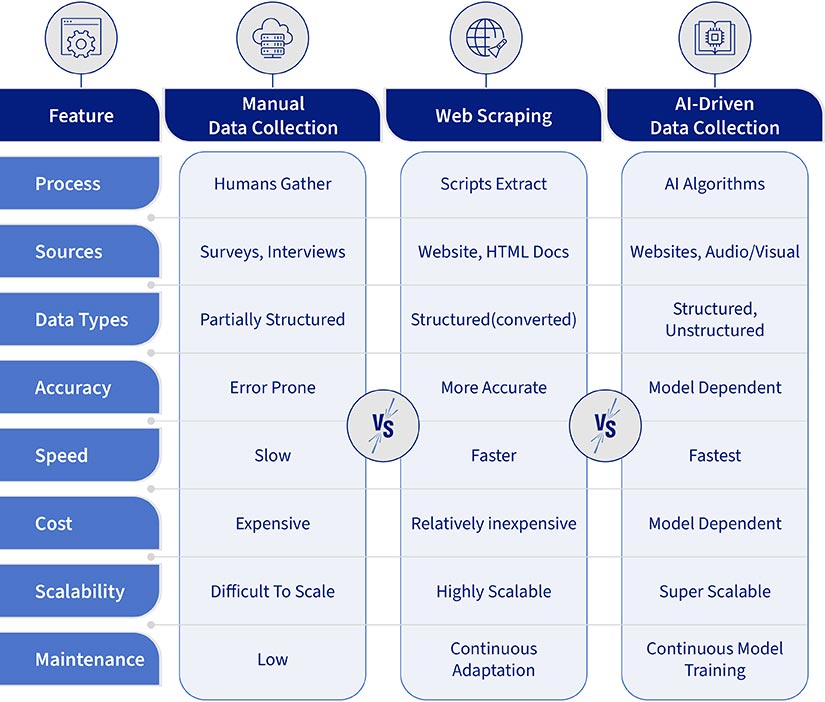
A Comparative Analysis of AI vs Web Scrapers vs Manual Data Collection
A comprehensive analysis of these data collection technologies, focusing on efficiency, speed, precision, scalability, cost implications, and ethical considerations, helps make informed decisions aligned with your data collection needs and strategic goals.
1. Efficiency and Speed
While you retain granular control, the challenges of manual data collection inherently limit your efficiency and speed. Manually copying and pasting data from websites or documents is time consuming and prone to human error. This method is thus impractical for large-scale data collection, especially when time is a critical factor.
Web scraping utilizes bots and scripts to carry out automated web data extraction based on your predefined parameters. This offers an advantage in speed and efficiency compared to manual methods. These bots navigate complex website structures and retrieve data much faster than human operators, enabling you to collect large datasets in shorter timeframes.
However, websites with dynamic content or anti-scraping measures can hinder web scraping, necessitating adjustments that may impact efficiency.
AI-powered data collection use machine learning algorithms to adapt to changes in website structures, circumvent anti-scraping techniques, and interpret unstructured data like text and images. This adaptability minimizes downtime and maximizes data collection efficiency, allowing for continuous and reliable data acquisition from complex and dynamic sources.
AI agents also learn to prioritize relevant data, reducing the need for manual filtering and further enhancing overall speed. These strategies contribute to effective data collection for real estate marketplaces.”
2. Accuracy and Scalability
Manual collection, while offering high accuracy for smaller datasets, often struggles to maintain consistency as data scales. The risk of human error increases exponentially with larger datasets. However, this method proves invaluable when you need to capture specific, nuanced data points that automated systems might miss.
Web scraping offers improved scalability compared to manual methods. However, it faces challenges due to changes in website structure and the implementation of anti-scraping measures.
The accuracy of this method depends on the scraper’s ability to navigate these dynamic elements and correctly parse the data. Consequently, data quality issues often arise in the form of missing values, format inconsistencies or incomplete data points.
Access to natural language processing (NLP) is one of the advantages of AI in data gathering, which helps extract and interpret data with greater accuracy than traditional web scraping. NLP enables AI models to understand the context and relationships within the data, resulting in more precise extraction.
This, combined with the ability to process vast amounts of data, also makes AI a highly scalable solution.
3. Cost Implications
The labor costs of manual data collection can become substantial, especially when you’re dealing with large-scale data acquisition. Manual data collection also introduces subjectivity and the potential for human error. This leads to extra costs associated with quality control and data cleansing.
Web scraping, especially when you use APIs, presents a more cost-effective approach. While the initial setup and scripting require technical expertise, the automated nature of web scraping reduces those ongoing labor costs. However, maintaining your scraping setup and adapting it to website changes can require additional investment.
AI-powered data collection reduces costs in the long run, but it requires a higher upfront investment. Developing, training and iterative refinement of AI models for accuracy demands specialized expertise and significant computational resources.
However, AI’’s ability to handle complex data structures and adapt to evolving data sources leads to long-term cost savings.
4. Ethical and Legal Considerations
Manual data collection, such as academic research involving human subjects, requires obtaining informed consent, maintaining privacy, and ensuring data security. Manual data collection is susceptible to researcher bias, which influences data selection and interpretation.
Researchers have a responsibility to secure storage, access control and proper data disposal. Ethical review boards and regulations like the GDPR provide the framework for these complexities.
Even when dealing with publicly available data, web scraping presents a complex legal situation. Websites utilize terms of service, robots.txt, and legal instruments such as the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act (CFAA) to regulate access and usage. Any scraping beyond authorized access, even for public data, involves serious legal consequences.
Ethical considerations also emerge concerning data ownership, potential harm to the website, and the implications of scraping sensitive information.
AI-powered data collection, while offering advanced capabilities, increases ethical concerns. Bias in training data can lead to discriminatory outcomes. AI’s ability to process vast datasets raises privacy concerns, especially with personally identifiable information (PII).
A crucial point is the distinction between data access and data use. While legal frameworks primarily address access (e.g., CFAA), ethical considerations extend to the use of collected data, regardless of the method.
HitechDigital aggregated, validated, and cleansed a database of 500,000 government contacts
HitechDigital aggregated, validated, and cleansed a database of 500,000 government contacts from 75,000 websites for a government procurement platform. This enhanced data accuracy to 99.5%, ensured integrity, and streamlined the sourcing process using a combination of manual verification and automated tools.
Read full Case Study »Use Cases and Applications – Manual Data Collection vs AI vs Web Scrapers
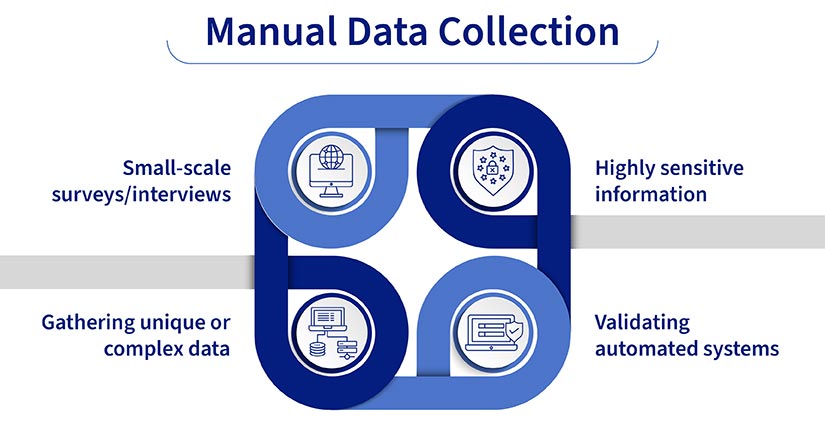
While automation offers efficiency, manual data collection still holds its place in specific scenarios in which human involvement is crucial for accuracy, nuance and security.
- Small-scale surveys/interviews: When dealing with a limited number of participants, direct interaction through interviews or paper surveys provides rich, qualitative data.
- Gathering unique or complex data: For information that isn’t easily captured digitally, like handwritten notes, diagrams or observations of physical behavior, manual collection is necessary.
- Highly sensitive information: When data security and privacy are prioritized, manual collection helps reduce the risks associated with digital breaches.
- Validating automated systems: Manual data collection is used to check the accuracy and reliability of automated data collection methods.
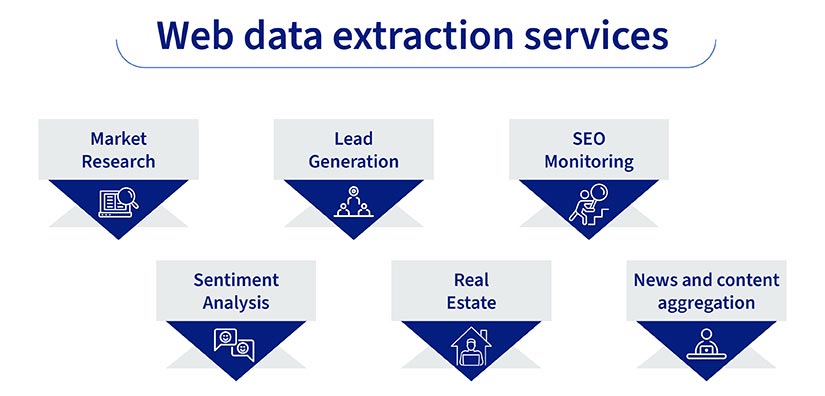
Here are a few examples of how web scraping can be applied. The specific use cases are limited only by the data available on the web and the user’s needs.
- Market research: Monitor pricing trends, competitor offerings, and customer reviews.
- Lead generation: Gather contact information for sales and marketing outreach.
- SEO monitoring: Track keyword rankings and website traffic.
- Sentiment analysis: Analyze social media and online reviews to understand public opinion.
- Real estate: Aggregate property listings and market data.
- News and content aggregation: Collect articles and updates from various sources.
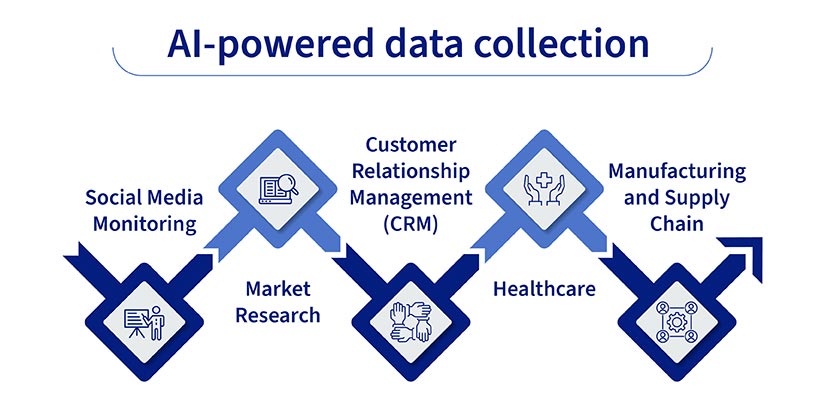
AI-powered data collection is changing how we gather and use information. Consider these examples:
- Social Media Monitoring: AI algorithms analyze social media posts, comments, and trends to understand public opinion and brand perception.
- Market Research: AI helps automate surveys, analyze customer feedback, and identify patterns in market data to guide business decisions.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): AI tools collect and analyze customer interactions, predict churn, and personalize customer experiences.
- Healthcare: Gather patient data from various sources, identify risk factors, and assist in diagnosis and treatment planning using AI.
- Manufacturing and Supply Chain: AI-powered sensors and systems monitor production lines, predict maintenance needs, and optimize logistics.
These examples highlight how AI is changing data collection across industries. The result is more efficient processes and data-driven insights.
HitechDigital implemented a scalable and flexible data aggregation workflow for a real estate company
HitechDigital implemented a scalable and flexible data aggregation workflow for a real estate company, processing 7M+ property records across 20+ county clerk websites. This reduced turnaround times from 3-4 days to 24 hours and provided significant cost savings by optimizing data extraction, validation, and entry processes.
Read full Case Study »How to Choose the Right Data Collection Method for Your Needs
When deciding on the right data collection method for your project, consider the following factors:
- Project scale: For small-scale data needs, manual extraction might suffice. However, large-scale data collection often necessitates web scraping or AI-powered tools for efficiency.
- Data complexity: Simple, structured data can be readily scraped. Complex, unstructured data, such as natural language from social media, often benefits from AI-powered sentiment analysis and entity recognition.
- Budget: Manual collection, while potentially accurate, is labor intensive and expensive at scale. Web scraping tools offer cost-effective solutions for large datasets. AI tools, while powerful, often carry a higher price tag.
- Time constraints: Manual extraction is slow. Web scraping offers faster data retrieval, especially for large volumes. AI tools can further expedite the process, particularly for complex data processing tasks.
- Accuracy requirements: Manual data collection, while susceptible to human error, offers high accuracy for small datasets. Web scraping accuracy depends on the scraper’s quality and website structure changes. AI tools can struggle with nuanced data interpretation.
Besides comparing AI and web scrapers for data collection against manual methods, it is also useful to follow a hybrid approach. For instance, a project might employ an AI-powered scraper to collect the bulk of the data and then use manual verification on a subset to ensure high accuracy.
Alternatively, web scraping can gather initial data, which then trains an AI model for further, more nuanced extraction.
Wrapping Up
When choosing a data collection method, consider your needs and limitations. Manual methods offer precision but are labor intensive and prone to error, best suited for small projects prioritizing quality.
Web scraping automates extraction but requires updates and raises ethical concerns. It’s ideal for large-scale collection within short timeframes.
AI tools offer adaptability and efficiency, handling complex data with high accuracy. Although the initial investment is high, long-term benefits make them compelling for large, dynamic projects.
Evaluate each method’s strengths and weaknesses by comparing them individually—AI vs. web scrapers, web scrapers vs. manual data collection, and AI data collection vs. traditional methods.
Careful consideration of their precision, speed, cost and ethical implications will help you select the best strategy that aligns with your objectives.
Automate data extraction with our expert web scraping solutions.
Let us handle the complexities of web scraping for you.






